Common Table Expression
In today’s SQL development, performance optimization is very important, especially when working with large datasets and complex queries. To address this, Common Table Expression(CTE) is one of the most effective tools in Query Tuning techinque. It temporarily stores the result of a query in memory, so you can use that data right away in the same batch of code. This makes your SQL easier to understand and helps your queries run more efficiently.
What is a Common Table Expression?
A Common Table Expression is a temporary result set that exists in memory for the duration of a single query batch. Think of it as a virtual table that stores the results of a query so that you can refer to them immediately afterward in the same statement.
The CTE exists only during the execution of the query and is not physically stored in the database. It helps reduce redundancy in your SQL code, and more importantly, it can significantly improve performance when used correctly.
Data Flow of Common Table Expression:
CTEs follow a three-phase process:
Phase 1 – Memory Indexing:
The base query is executed, and the resulting data is stored in a memory block associated with the CTE name. This is a temporary storage phase.
Phase 2 – In-Memory Operations:
Once the data is stored, SELECT or DML (Data Manipulation Language) operations are performed directly on this in-memory data. Since this avoids disk I/O, operations run much faster.
Phase 3 – Commit to Database:
Any changes made to the in-memory data can then be committed to the base table. This ensures data consistency while still leveraging the performance of in-memory processing.
Benifits of using Common Table Expression:
CTEs are not just for simplifying code—they also bring significant performance benefits:
Faster Execution for Large Data Sets:
For operations involving millions of rows, executing the logic in memory before hitting the base table can save significant processing time.Improved Code Readability:
SQL code becomes modular and easy to understand, especially when dealing with nested or recursive queries.Scoped Execution:
Since CTEs are only accessible within their query batch, they don’t interfere with other parts of your application or stored procedures.Safe Testing Zone:
Developers can test complex operations on a virtual dataset without modifying the actual table until the final commit.
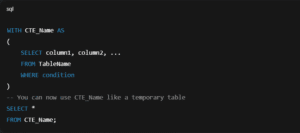
Syntax for CTE:
Want to Master SQL and Unlock High-Paying Data Roles?
Join SQL School — India’s leading real-time training institute for SQL Server and T-SQL development.
✅ Learn SQL Server 2019 & 2022 step-by-step
✅ Master complex queries, joins, subqueries, indexing, and performance tuning
✅ Work on real-time projects with live enterprise servers
✅ Hands-on experience with SSMS, stored procedures, triggers, and optimization
📞 Call Now: +91 96666 40801
🌐 Visit: www.sqlschool.com for a FREE Demo Session
SQL School – Your Real-Time Guide to SQL Server Mastery & Career Success.
