🚀 Launch Your Career: The Essential Database Intro for Aspiring Data Professionals
Welcome to the starting line of a rewarding journey into the world of data! Whether you’re aiming to become a Database Administrator, a Data Engineer, or a Data Analyst, understanding the core foundation of databases is non-negotiable. This comprehensive guide, based on an expert-led introductory session, will break down the entire data ecosystem—from what a database is and the types of data stores (OLTP vs. Data Warehouse) to the critical Database Job Roles that drive modern technology. Get ready to equip yourself with the knowledge to make an informed and strategic career choice.
📺 The Foundation: Watch the Video Walkthrough
This video provides an excellent, detailed overview of the database workflow, core concepts, and the distinct professional paths available in the industry.
Don’t miss future sessions! Hit the subscribe button and click the bell 🔔 to get notified!
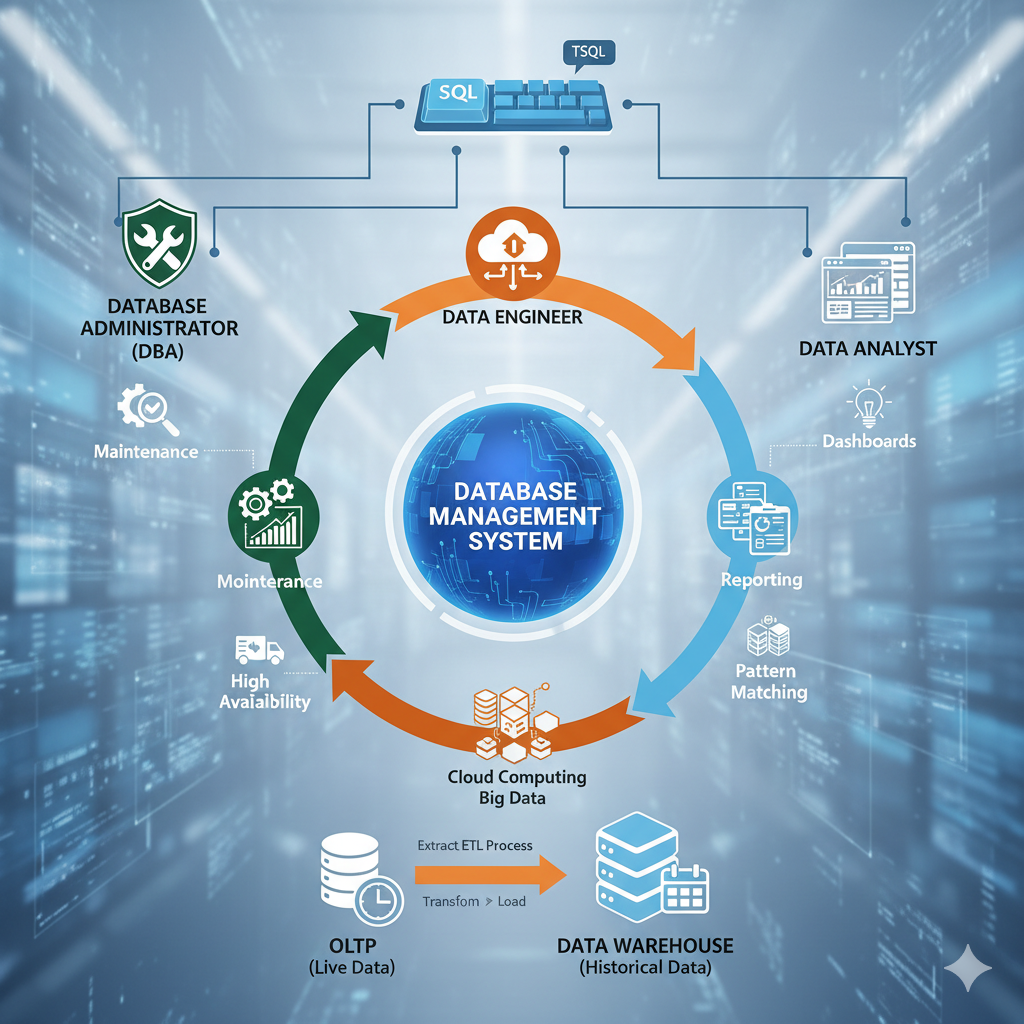
What’s On Deck: Deconstructing the Database Ecosystem
To master the data landscape, you must first understand its components and how they interact. Here is a breakdown of the video’s core concepts:
⚙️ Core Concepts: Database and DBMS
A solid foundation starts with definitions. The concept of a database extends far beyond a simple file storage system:
- A Database is a platform designed to store any type and any amount of data [08:52]. It is secured, easy to organize, and supports unlimited data, cloud computing, and AI environments [09:15].
- A DBMS (Database Management System) is the specialized software used to build, design, manage, and access the database [11:29].
- Examples of DBMS include Oracle, SQL Server, Postgress, and IBM DB2 [12:21]. SQL Server is often preferred for its comparative ease of implementation and cost.
📊 Two Sides of Data: OLTP vs. Data Warehouse
Not all data is treated equally; it’s segregated based on its age and activity level, much like separating a house’s living room from its storage room [16:50]:
- OLTP (Online Transaction Processing): This is the “living room” database.
- Stores live, real-time data (e.g., live stock market, live temperatures) [13:13].
- Developers are primarily involved in its design.
- Data Warehouse (DWI): This is the “store room” or “godown” database.
- Stores historical, old, and inactive data[13:35].
- Data Engineers are primarily involved in its design.
🛣️ The End-to-End Data Workflow
Data moves from its origin to its final reporting destination through a clear pipeline [14:42]:
- Data Birthplace: Sources like websites, apps, or files (Excel, flat files, JSON) feed the data stream.
- Active Data: Data is first housed in the OLTP database (e.g., MSSQL, Oracle).
- Data Transport: Data Engineers use ETL (Extract, Transform, Load)—the “transport system”—to read data from OLTP and write it to the Data Warehouse [17:35]. This is often tied to Cloud Computing and Big Data [18:39].
- Reporting/Analytics: Data Analysts read the data from both OLTP and the Data Warehouse to generate reports, dashboards, and perform pattern matching [17:55].

🔑 Essential Tools & Prerequisites
To start your hands-on practice, you’ll need the right language and the right environment:
- SQL (Structured Query Language): This is the fundamental language used for every touch on a database—to store, read, analyze, and administer data [22:01].
- TSQL (Transact-SQL): A specific brand or dialect of SQL designed by Microsoft, used to interact with SQL Server [22:45].
- SSMS (SQL Server Management Studio) Tool: A graphical tool needed to access and manage your SQL Servers, similar to how a browser accesses a website [48:10], [53:05].
- Practice Setup: It’s recommended to install minimum two servers (e.g., SQL Server 2022 and 2019) to practice advanced concepts like remote joins [46:04], [46:31].
💡Hands-On Challenge / Practical Tip
A core activity for a Data Engineer is handling the data transport system that moves old data from the OLTP system into the Data Warehouse. What is the name of this three-stage process, and what do the letters stand for?
Hint: Quick Tip
The name of the process is an acronym. Its function is to take raw data, clean or change it, and then store it in the destination.
Solution: Detailed Answer
The process is called ETL. It stands for:
E - Extract (Reading data from the source, typically OLTP)
T - Transform (Changing, cleaning, or aggregating the data)
L - Load (Writing the data to the destination, typically a Data Warehouse)
This is a foundational concept in data engineering and cloud computing.
🌟Why This Matters: Choosing Your Career Path
Understanding the distinctions between Database Job Roles is crucial, as the required skills and focus areas are entirely different [35:07]:
- Database Administrator (DBA): Focuses on maintenance, monitoring, troubleshooting, and high availability—acting as the “database doctor” [34:06]. Their SQL learning should focus on repairing and tuning.
- Data Engineer: Focuses on data pipelines, cloud computing, and Big Data (ETL). Their SQL learning should focus on efficient querying and loading.
- Data Analyst: Focuses on reporting, dashboard creation (e.g., PowerBI), and trend analysis. Their SQL learning should focus on analyzing and retrieving data.
Being specific about your target role (DBA, Engineer, or Analyst) is the key to mastering only the required 15-20% of the vast SQL world and achieving your career goals faster.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is the difference between SQL and TSQL?
SQL (Structured Query Language) is the universal, standard language for communicating with databases. TSQL (Transact-SQL) is a specific implementation (a “brand”) of SQL developed by Microsoft for use with SQL Server. Think of SQL as the category “Mobile Phone” and TSQL as the brand “iPhone” [22:51].
Do I need to learn ‘complete SQL’ to get a data job?
No. The video emphasizes that learning “complete SQL” (which can take four to six months) is typically for developers [39:40]. For a specific role like DBA, Data Engineer, or Data Analyst, you only need to focus on the SQL concepts relevant to your job role (e.g., tuning for a DBA, querying for an Engineer) [40:04]. Being target-oriented is the smartest way to succeed.
What software do I need to start practicing SQL?
To start your hands-on practice, you need to install the SQL Server itself (versions 2022 and 2019 are recommended) and the graphical client tool called SSMS (SQL Server Management Studio) [45:45]. A Windows OS (version 8 or higher, preferably not Home Edition) is required for full functionality [48:51].
🎯 Summary Snapshot Table
| Focus Area | Key Takeaway | Your Action Step |
|---|---|---|
| Database Type | OLTP is for live, active data; Data Warehouse is for historical data. | Understand which data store you will primarily interact with in your target role. |
| Data Job Role | Your career path (DBA, Engineer, Analyst) determines your required SQL skill set. | Choose a specific role today to narrow your learning focus and avoid burnout. |
| Essential Tool | The language of data is SQL/TSQL, and the interface tool is SSMS. | Begin the installation process for SQL Server (2022/2019) and SSMS immediately. |
✨ Final Thoughts: The Time to Act is Now
The field of databases is dynamic, with continuous advancements in Cloud, AI, and Big Data. But all these technologies rely on the fundamental concepts discussed here. Your journey requires commitment, practice, and the right guidance. By prioritizing your learning based on a target Database Job Role, you transform a vast subject into a focused, achievable goal. You do more, you get more! [05:02] Keep practicing, submit your assignments, and stay engaged.
Ready to take the next step? Dive into the hands-on practice of SQL basics and start building the skills that will make you indispensable in your new career!