Master SQL Fundamentals: Key Concepts Every Learner Should Know
Data powers every modern system—and SQL is the language that brings data to life. Whether you’re working with applications, reports, or enterprise systems, SQL allows you to interact with databases in a clear and controlled way.
This guide explains the most important SQL concepts in a practical, easy-to-follow manner, helping both beginners and professionals strengthen their database skills.
Why SQL Matters in Today’s Technology World
SQL is the standard language for managing relational databases. It is trusted because it is:
Simple to read and write
Supported by all major database platforms
Scalable for small and large systems
Reliable for mission-critical applications
Understanding SQL concepts enables you to work confidently with data and make informed decisions using real information.
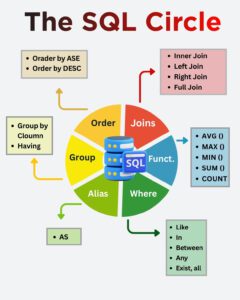
Filtering Data with the WHERE Clause
The WHERE clause controls which rows are returned from a table. Instead of retrieving all data, it allows you to focus only on what matters.
Commonly Used Conditions:
LIKEfor pattern searchesINfor selecting multiple valuesBETWEENfor range-based filteringEXISTSfor advanced comparisons
Key Benefits:
Faster query performance
Cleaner and more precise results
Essential for handling large datasets
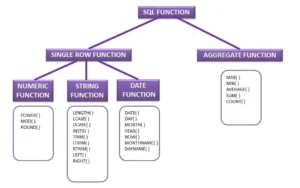
SQL Functions: Turning Raw Data into Insights
SQL functions play a vital role in converting raw database records into meaningful and actionable information. Instead of manually analyzing large datasets, SQL functions allow you to perform calculations, summaries, and comparisons directly within the database, saving time and improving efficiency.
Frequently Used SQL Functions
COUNT():
Counts the number of rows in a table or result set. It is commonly used to measure volume, such as the total number of customers, orders, or transactions.SUM():
Calculates the total of a numeric column. This function is often used for financial data, such as total sales, revenue, or expenses.AVG():
Computes the average value of a numeric column. It helps analyze trends, such as average salary, average order value, or average performance metrics.MIN() and MAX():
Identify the smallest and largest values in a dataset. These functions are useful for comparisons, such as finding the lowest price, highest score, or earliest and latest dates.
Why SQL Functions Are Important
Used in Reports and Dashboards
Enable Quick Data Analysis
Reduce Manual Calculations
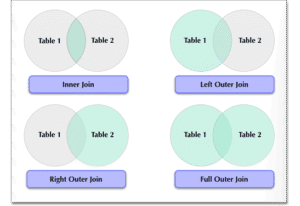
Joining Tables to Build Complete Information
In real-world database systems, information is usually distributed across multiple tables to avoid redundancy and improve data integrity. SQL JOINS make it possible to combine related data from these tables into a single, meaningful result set. By using joins, you can retrieve complete information that would otherwise be scattered across different tables.
Common Join Types:
INNER JOIN – INNER JOIN is commonly used when only related and complete data is required.
LEFT JOIN – LEFT JOIN is useful when you want complete data from one table even if related data is missing.
RIGHT JOIN – This join is helpful when the focus is on preserving all records from the right-side table.
FULL JOIN – Returns all records from both tables, including matching and non-matching rows. FULL JOIN is useful for comparing datasets and identifying gaps between tables.
Practical Advantages:
Enables relational database design
Supports complex queries
Essential for enterprise applications
GROUP BY
The GROUP BY clause groups rows that share the same values in one or more columns. Once the data is grouped, SQL aggregate functions such as COUNT()SUM()AVG()MIN()MAX() can be applied to each group to produce summarized results.
GROUP BY is commonly used when you want to analyze data by categories rather than individual records.
HAVING
The HAVING clause is used to filter grouped data after aggregation has taken place. Unlike the WHERE clause, which filters rows before grouping, HAVING works on grouped results and is ideal for applying conditions on aggregated values.
HAVING is especially useful when you need to filter results based on calculations such as totals, averages, or counts.
Real-Life Examples
Total Sales by Region:
Helps organizations understand which regions are performing well and which require improvement.Employee Count per Department:
Assists HR and management teams in workforce planning and resource allocation.Monthly Revenue Analysis:
Enables finance teams to track business growth, identify trends, and make data-driven decisions.
Using ALIAS for Cleaner Queries
An ALIAS in SQL is a temporary name assigned to a column or a table within a query. It does not change the actual name stored in the database but is used only for the duration of the query execution. Aliases make SQL queries easier to read, understand, and maintain, especially when working with complex statements or long column names.
Aliases are commonly created using the AS keyword, though using AS is optional in most databases.
Why Alias Is Useful
Improves Readability:
Long or technical column names can make queries difficult to understand. Using aliases helps present cleaner and more meaningful names, making the query logic easier to follow.Makes Reports User-Friendly:
Aliases allow you to display clear and business-friendly column headings in reports and query results, which is especially helpful for non-technical users.Simplifies Complex SQL Statements:
When working with joins, subqueries, or calculated fields, aliases reduce repetition and shorten query syntax, making complex SQL queries easier to write and manage.
Sorting Results with ORDER BY
The ORDER BY clause is used to organize the result set of a SQL query into a specific and meaningful sequence. By default, data retrieved from a table has no guaranteed order. ORDER BY allows you to control how records are displayed, making the output easier to read, analyze, and present.
Sorting can be applied to one or multiple columns and plays a key role in reporting and data analysis.
Sorting Options
Ascending (ASC):
Sorts the data from the lowest value to the highest value.
For numbers, this means small to large; for text, it follows alphabetical order (A to Z); and for dates, it shows the oldest records first.
Ascending order is the default sorting method in SQL.Descending (DESC):
Sorts the data from the highest value to the lowest value.
This is commonly used when you want to view top-performing records, recent entries, or highest values first.
Use Cases of ORDER BY
Ranking Results:
Helps identify top or bottom performers, such as highest salaries, best-selling products, or maximum scores.Displaying Reports:
Ensures reports are well-structured and easy to understand by presenting data in a consistent order.Improving Data Clarity:
Makes large datasets more readable by organizing records logically, reducing confusion and improving decision-making.
Key Features of SQL as a Language
✔ Easy syntax
✔ High performance
✔ Secure and reliable
✔ Compatible with many platforms
✔ Industry-wide acceptance
Advantages of Learning SQL Concepts
Strong foundation for data careers
Required skill for developers and analysts
Helps understand database behavior
Improves problem-solving skills
Opens opportunities in multiple domains
Who Should Learn SQL?
SQL is ideal for:
Beginners entering IT
Software developers
Database administrators
Data analysts and engineers
Business intelligence professionals
Conclusion
SQL concepts are the building blocks of modern data systems. By understanding how filtering, joining, grouping, and sorting work together, you gain the ability to handle real-world data efficiently.
Mastering SQL fundamentals is not just about learning commands—it’s about learning how data works.
MSSQL Training: https://sqlschool.com/sql-server-training/
MSSQL Curriculum: https://sqlschool.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/12/SQL-Server-TSQL-Training.pdf
#SQL #SQLFundamentals #LearnSQL #SQLBasics #DatabaseConcepts #RelationalDatabase #SQLQueries #SQLFunctions #SQLJoins #WhereClause #GroupBy #OrderBy #DataAnalytics #DataSkills #BusinessIntelligence #ITCareers #TechSkills
Trainer: Mr. Sai Phanindra
With 19+ Years of
technical expertise exclusively on SQL & Database Technologies, I assure you 100% Practical, Step by Step Classes.
Linkdin Profile: www.linkedin.com/in/saiphanindra/
Contact No: +91 9030040801 or +91 9666640801